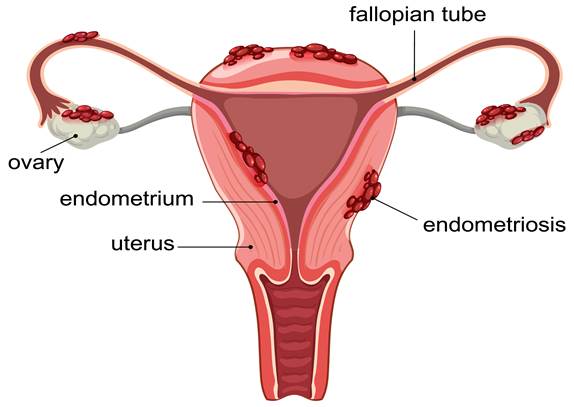
What is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it. This tissue can cause pain, heavy periods, and sometimes trouble getting pregnant. Although it is common, many people do not know they have it. Often, symptoms can be mild or mistaken for other problems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), endometriosis affects about 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide.
What Does Surgery for Endometriosis Involve?
Surgery for endometriosis aims to remove or destroy the extra tissue. Doctors may use a method called laparoscopy, which is a type of keyhole surgery. During this procedure, small cuts are made in the belly. Then, the doctor uses special tools to remove or burn away the endometriosis tissue. Sometimes, more extensive surgery is needed if the tissue is widespread. Surgery can help relieve pain and improve quality of life. However, it may not cure endometriosis completely.
Can Endometriosis Come Back After Surgery?
Yes, endometriosis can come back after surgery. This is called endometriosis recurrence after surgery. Even though surgery removes visible tissue, small bits may remain. Over time, these can grow again. Studies show that the recurrence of endometriosis can happen in up to 50% of cases within five years. The risk of endometriosis returning depends on several factors. Therefore, it is important to keep regular follow-ups with your doctor after surgery.
Factors Influencing Recurrence
Several things can affect the risk of endometriosis coming back after surgery. For example, the type of surgery and how much tissue was removed matter. Other factors include:
Age at the time of surgery
Severity and stage of endometriosis
Whether all visible tissue was removed
Hormone levels and menstrual cycles
Not using hormone therapy after surgery
Family history of endometriosis
Because each person is different, your doctor will discuss your personal risk with you.
Signs and Symptoms of Recurrence
After surgery, it is important to watch for signs that endometriosis may be returning. Common symptoms include:
Painful periods
Pelvic pain between periods
Pain during sex
Pain when using the bathroom
Heavy or irregular periods
Trouble getting pregnant
If you notice these symptoms, it does not always mean endometriosis is back. However, you should talk to your doctor for advice.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While you cannot always prevent endometriosis recurrence, some steps may help lower the risk. For instance, your doctor may suggest hormone therapy after surgery. This can help slow the growth of new tissue. In addition, healthy habits can support your well-being. Try these tips:
Maintain a healthy weight
Exercise regularly
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
Manage stress with relaxation techniques
Take medicines as prescribed
Although these steps may not stop recurrence, they can help you feel better overall.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to stay in touch with your healthcare provider after surgery. If you notice new or worsening symptoms, do not wait. For example, if you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, or trouble with daily activities, see your doctor soon. Early treatment can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. Regular check-ups are also important, even if you feel well.
Consult a gynecologist for personalized advice about endometriosis management and recurrence.
