Introduction
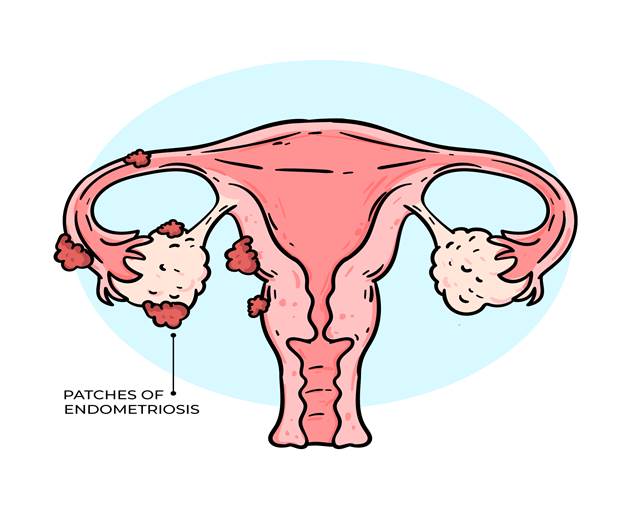
Getting diagnosed with endometriosis can feel overwhelming. Endometriosis is a condition where tissue, similar to the lining of the uterus, grows outside the uterus. This can cause pain, heavy periods, and other symptoms. However, a diagnosis is the first step toward better care. Now, you can start learning about your options and plan your next steps after endometriosis diagnosis.
Immediate Steps After Diagnosis
After you are diagnosed with endometriosis, your doctor will explain what the condition means for you. Usually, you will discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any concerns. Next, your doctor may suggest more tests or refer you to a specialist. It is important to ask questions and write down any advice. This helps you remember important details later. You may also receive information about endometriosis treatment options at this stage.
Common Symptoms and Their Management
Endometriosis can cause several symptoms. Some of the most common include:
Painful periods
Pelvic pain between periods
Pain during sex
Heavy bleeding
Trouble getting pregnant
To manage these symptoms, you can try a few simple steps. For example, using a heating pad may help ease cramps. Over-the-counter pain medicine, like ibuprofen, can also reduce pain. However, always talk to your doctor before starting any new medicine. In some cases, your doctor may suggest hormone therapy or other treatments to help control symptoms.
Diagnostic Follow-Up
After your diagnosis, follow-up visits are important. Your doctor may order more tests, such as:
Ultrasound scans to check for cysts
Blood tests to rule out other problems
Referral to a gynecologist or pain specialist
These steps help your doctor understand how endometriosis affects you. As a result, you will get a treatment plan that fits your needs. Be sure to attend all follow-up appointments and share any new symptoms.
Treatment Options
There are several endometriosis treatment options. Your doctor will help you choose the best one. Some common treatments include:
Medications: Pain relievers and hormone therapy can help control symptoms.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery removes endometriosis tissue. This can reduce pain and improve fertility.
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can make a difference.
Each person is different. Therefore, your treatment may change over time. Always discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before making decisions.
Emotional and Lifestyle Guidance
Living with endometriosis can affect your emotions and daily life. It is normal to feel worried or stressed. However, you are not alone. Many people find support in talking with friends, family, or support groups. Joining a support group can help you share experiences and learn new coping tips. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or yoga, may help reduce stress. Remember, taking care of your mental health is just as important as managing physical symptoms.
Prevention and Long-Term Outlook
While there is no way to prevent endometriosis, you can lower the risk of complications. For example, regular check-ups help catch problems early. Following your treatment plan also keeps symptoms under control. Over time, some people may see their symptoms improve, while others may need ongoing care. With the right support, many people live full and active lives with endometriosis.
When to Seek Further Help
Sometimes, symptoms can get worse or new problems may appear. You should contact your doctor if you notice:
Severe pain that does not improve
Heavy bleeding that soaks through pads or tampons quickly
Fever, nausea, or vomiting
Trouble passing urine or stool
If you have any of these red flags, seek medical help right away. Early treatment can prevent serious problems.
Conclusion
Being diagnosed with endometriosis is the start of your journey to better health. There are many ways to manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. For the best results, consult a specialist for personalized guidance on managing endometriosis.
